How To Set Up Search Engine Optimization
This guide will be an introduction to and overview of search engine optimization (SEO), a hugely important tactic for driving traffic to your site.
In this guide you'll larn:
- What is SEO & Why is it Of import?
- SEO Keyword Research & Keyword Targeting Best Practices
- On-Page Optimization Best Practices
Let's get started!
1. What is SEO & Why is information technology Important?
Search engine optimization is the process of optimizing web pages and their content to be hands discoverable by users searching for terms relevant to your website. The term SEO too describes the process of making web pages easier for search engine indexing software, known as "crawlers," to find, scan, and index your site.
While the concept of SEO is relatively straightforward, many newcomers to SEO withal accept questions about the specifics, such as:
- How do you "optimize" for your site or your company's site for search engines?
- How do you know how much time to spend on SEO?
- How can you differentiate "proficient" SEO advice from "bad" or harmful SEO advice?
Perhaps the nigh important attribute of search engine optimization is how you can actually leverage SEO to aid drive more relevant traffic, leads, and sales for your business concern.
Why Should You Care Virtually SEO?
Billions of searches are conducted online every single day. This means an immense amount of specific, high-intent traffic.
Many people search for specific products and services with the intent to pay for these things. These searches are known to havecommercial intent, meaningthey are clearly indicating with their search that they want to buy something you offer.

A search query like "car dealerships well-nigh me" displays articulate commercial intent
People are searching for any manner of things straight related to your business. Beyond that, your prospects are too searching for all kinds of things that are simply loosely related to your business. These correspond even more opportunities to connect with those folks and help answer their questions, solve their problems, and become a trusted resource for them.
Are you more than probable to get your widgets from a trusted resource who offered neat data each of the terminal iv times you turned to Google for assist with a problem, or someone you've never heard of?
Is your site optimized for search? Go a free SEO audit with the free LOCALiQ website grader.
WhatActually Works for Driving SEO Traffic from Search Engines?
Information technology's important to annotation that Google is responsible for the bulk of the search engine traffic in the world. This may vary from one industry to another, but information technology'south likely that Google is the dominant actor in the search results that your concern or website would want to prove up in, but the all-time practices outlined in this guide will help you lot to position your site and its content to rank in other search engines, as well.
So how does Google make up one's mind which pages to return in response to what people search for? How do you go all of this valuable traffic to your site?
Google'southward algorithm is extremely circuitous, but at a loftier level:
- Google is looking for pages that incorporate high-quality, relevant data relevant to the searcher'southward query.
- Google's algorithm determines relevance past "crawling" (or reading) your website's content and evaluating (algorithmically) whether that content is relevant to what the searcher is looking for, based on the keywords it contains and other factors (known every bit "ranking signals").
- Google determines "quality" by a number of means, but a site's link profile – the number and quality of other websites that link to a page and site as a whole – is among the about important.
Increasingly, boosted ranking signals are existence evaluated past Google's algorithm to determine where a site volition rank, such as:
- How people engage with a site (Practise they find the information they need and remain on the site, or do they "bounciness" dorsum to the search page and click on some other link? Or practice they but ignore your listing in search results altogether and never click-through?)
- A site's loading speed and "mobile friendliness"
- How much unique content a site has (versus "sparse" or duplicated, low-value content)
There are hundreds of ranking factors that Google's algorithm considers in response to searches, and Google is constantly updating and refining its process to ensure that information technology delivers the best possible user feel.
ii. SEO Keyword Research & Keyword Targeting Best Practices
The first stride in search engine optimization is to determine what yous're actually optimizing for. This waysidentifying terms people are searching for, also known as "keywords," that you lot want your website to rank for in search engines like Google.
For case, yous may want your widget company to show up when people look for "widgets," and peradventure when they type in things similar "purchase widgets." The effigy below shows search volume, or the estimated number of searches for a specific term, over a period of fourth dimension:
Tracking SEO keywords across various time periods
There are several cardinal factors to take into account when determining the keywords yous desire to target on your site:
- Search Book – The first factor to consider is how many people are actually searching for a given keyword. The more people at that place are searching for a keyword, the bigger the potential audience you stand to reach. Conversely, if no 1 is searching for a keyword, at that place is no audience available to observe your content through search.
- Relevance – A term may exist frequently searched for, but that does not necessarily mean that information technology is relevant to your prospects. Keyword relevance, or the connection between content on a site and the user's search query, is a crucial ranking signal.
- Competition – Keywords with higher search volume tin can bulldoze significant amounts of traffic, simply competition for premium positioning in the search engine results pages can be intense.
Get-go yous need to understand who your prospective customers are and what they're likely to search for. From there you need to sympathize:
- What types of things are they interested in?
- What problems exercise they accept?
- What blazon of language do they utilize to describe the things that they do, the tools that they utilize, etc.?
- Who else are they buying things from?
In one case you lot've answered these questions, you'll have an initial "seed list" of possible keywords and domains to help you lot observe additional keyword ideas and to put some search volume and competition metrics around.
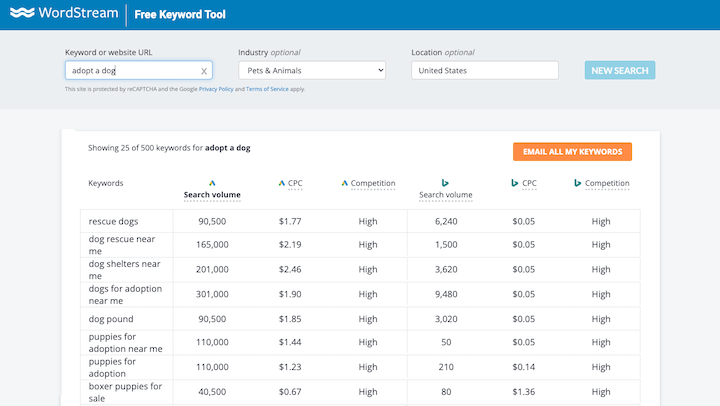
Have the list of core ways that your prospects and customers describe what you lot exercise, and start to input those into keyword tools like Google's own keyword tool or tools similar WordStream's keyword tool:
WordStream'southward Gratuitous Keyword Tool for SEO
Additionally, if y'all have an existing site, you're likely getting some traffic from search engines already. If that'south the case, you tin utilise some of your ain keyword data to help you understand which terms are driving traffic (and which you might be able to rank a bit better for).
Unfortunately, Google has stopped delivering a lot of the information about what people are searching for to analytics providers. Google does make some of this data available in their free Webmaster Tools interface (if you lot haven't set up an business relationship, this is a very valuable SEO tool both for unearthing search query information and for diagnosing various technical SEO issues).
Once y'all've taken the time to empathise your prospects, accept looked at the keywords driving traffic to your competitors and related sites, and have looked at the terms driving traffic to your ain site, you need to work to understandwhich terms y'all can conceivably rank for andwhere the best opportunities actually lie.
Determining the relative contest of a keyword can exist a fairly circuitous task. At a very loftier level, yous demand to understand:
- How trusted and administrative (in other words: how many links does the whole site get, and how loftier quality, trusted, and relevant are those linking sites?) other entire sites that volition be competing to rank for the aforementioned term are
- How well aligned they are with the keyword itself (do they offering a great answer to that searcher'southward question)
- How popular and administrative eachindividual folio in that search result is (in other words: how many links does the page itself have, and how high quality, trusted, and relevant are those linking sites?)
Yous can dive deeper into the procedure of determining how competitive keywords are by using WordStream founder Larry Kim'due south competitive index formula.
iii. On-Page Optimization for SEO
In one case you have your keyword list, the adjacent step is actually implementing your targeted keywords into your site'south content. Each page on your site should be targeting a core term, as well every bit a "handbasket" of related terms. In his overview of the perfectly optimized page, Rand Fishkin offers a nice visual of what a well (or perfectly) optimized page looks similar:
The "Perfectly Optimized Folio" (via Moz)
Permit'due south look at a few critical, bones on-page elements you'll want to empathise as y'all think most how to bulldoze search engine traffic to your website:
Title Tags
While Google is working to better understand the actual significant of a page and de-emphasizing (and even punishing) aggressive and manipulative utilize of keywords, including the term (and related terms) that you want to rank for in your pages is still valuable. And the single virtually impactful place you can put your keyword is your page's title tag.
The title tag isnon your page's principal headline. The headline y'all run across on the page is typically an H1 (or perchance an H2) HTML element. The championship tag is what you lot can see at the very top of your browser, and is populated past your page's source code in a meta tag:
Your title tag matches your organic outcome headline: Make information technology clickable
The length of a championship tag that Google will show volition vary (it'south based on pixels, not character counts) but in full general 55-60 characters is a adept rule of thumb here. If possible you want to work in your core keyword, and if you lot tin can do information technology in a natural and compelling way, add some related modifiers effectually that term likewise. Keep in mind though: the title tag will oft be what a searcher sees in search results for your folio. It'due south the "headline" in organic search results, so you besides want to have how clickable your title tag is into account.
Meta Descriptions
While the title tag is finer your search listing's headline, the meta description (another meta HTML element that tin can be updated in your site'due south code, but isn't seen on your bodily page) is effectively your site'southward additional ad copy. Google takes some liberties with what they brandish in search results, and then your meta description may not always prove, only if you have a compelling description of your page that would make folks searching likely to click, you can greatly increase traffic. (Remember: showing up in search results is just the showtime step! You lot nonetheless need to get searchers to come to your site, then actually take the action y'all want.)
Here's an instance of a real-globe meta clarification showing in search results:
Meta descriptions = SEO "advertizement re-create"
Include a concise description of the tool, a clear benefit, and a call to action, like Google advertisement copy!
Body Content
The actual content of your folio itself is, of course, very important. Different types of pages will have different "jobs" – your cornerstone content nugget that you lot want lots of folks to link to needs to be very unlike than your support content that y'all want to make sure your users find and get an answer from quickly. That said, Google has been increasingly favoring sure types of content, and as you build out whatever of the pages on your site, there are a few things to keep in heed:
- Thick & Unique Content – There is no magic number in terms of word count, and if you accept a few pages of content on your site with a scattering to a couple hundred words y'all won't be falling out of Google's good graces, but in full general recent Panda updates in particular favor longer, unique content. If you have a large number (think thousands) of extremely short (50-200 words of content) pages or lots of duplicated content where nothing changes only the folio'southward title tag and say a line of text, that could get you in problem. Look at the entirety of your site: are a large percentage of your pages thin, duplicated and depression value? If so, try to identify a way to "thicken" those pages, or check your analytics to meet how much traffic they're getting, and only exclude them (using a noindex meta tag) from search results to keep from having it appear to Google that y'all're trying to flood their index with lots of low value pages in an try to have them rank.
- Date – Google is increasingly weighting engagement and user experience metrics more heavily. Yous can impact this past making certain your content answers the questions searchers are asking and so that they're probable to stay on your page and engage with your content. Make sure your pages load apace and don't have blueprint elements (such every bit overly aggressive ads to a higher place the content) that would be likely to turn searchers off and ship them abroad.
- "Sharability" – Not every single piece of content on your site volition be linked to and shared hundreds of times. But in the same style you want to be careful of not rolling out big quantities of pages that have thin content, you want to consider who would exist likely to share and link to new pages you're creating on your sitebefore you scroll them out. Having large quantities of pages that aren't likely to exist shared or linked to doesn't position those pages to rank well in search results, and doesn't aid to create a good moving-picture show of your site as a whole for search engines, either.
Alt Attributes
How you mark up your images tin impact not only the manner that search engines perceive your page, just too how much search traffic from epitome search your site generates. An alt attribute is an HTML element that allows you to provide culling information for an image if a user can't view it. Your images may break over time (files get deleted, users have difficulty connecting to your site, etc.) so having a useful description of the paradigm can be helpful from an overall usability perspective. This also gives you another opportunity – exterior of your content – to help search engines understand what your page is virtually.
You don't want to "keyword stuff" and cram your core keyword and every possible variation of information technology into your alt aspect. In fact, if information technology doesn't fit naturally into the description, don't include your target keyword here at all. Just be sure not to skip the alt attribute, and endeavour to requite a thorough, accurate clarification of the image (imagine you're describing it to someone who can't see it – that's what information technology'south there for!).
By writing naturally about your topic, you're avoiding "over-optimization" filters (in other words: it doesn't make it look like you're trying to trick Google into ranking your page for your target keyword) and you give yourself a better chance to rank for valuable modified "long tail" variations of your core topic.
URL Structure
Your site's URL structure tin exist important both from a tracking perspective (y'all can more hands segment information in reports using a segmented, logical URL construction), and a shareability standpoint (shorter, descriptive URLs are easier to copy and paste and tend to go mistakenly cutting off less ofttimes). Again: don't work to cram in as many keywords every bit possible; create a short, descriptive URL.
Moreover: if you don't have to, don't change your URLs. Even if your URLs aren't "pretty," if you don't feel as though they're negatively impacting users and your business in full general, don't change them to be more than keyword focused for "better SEO." If you practise accept to change your URL structure, brand sure to utilize the proper (301 permanent) type of redirect. This is a common mistake businesses make when they redesign their websites.
Schema & Markup
Finally, once you take all of the standard on-page elements taken care of, you can consider going a step farther and ameliorate helping Google (and other search engines, which also recognize schema) to understand your page.
Schema markup does non make your page show up higher in search results (it's non a ranking factor, currently). Information technology does give your listing some additional "real estate" in the search results, the fashion ad extensions do for your AdWords ads.
In some search results, if no 1 else is using schema, y'all tin can go a overnice advantage in click-through rate by virtue of the fact that your site is showing things like ratings while others don't. In other search results, where everyone is using schema, having reviews may be "table stakes" and you might be hurting your CTR by omitting them:
Beget your organic results more than existent estate by calculation markup and schema
At that place are a variety of different types of markup you can include on your site – most probably won't apply to your business, but information technology's likely that at to the lowest degree i form of markup will apply to at least some of your site's pages.
Y'all can learn more about schema & markup in WordStream's guide to schema for SEO.
Farther SEO Reading & Resources
This guide is intended to serve as an introduction to SEO. For a more than in-depth overview of content creation for SEO, the technical considerations of which you lot should be aware, and other related topics:
- Read Tom Demers' comprehensive introductory guide to SEO basics.
- Check out LOCALiQ Marketing Lab's Local SEO course.
- Follow our piece of cake 10-step SEO audit.
- Explore these 11 free website graders for SEO and more.
- Get a free SEO audit with the LOCALiQ website grader
How To Set Up Search Engine Optimization,
Source: https://www.wordstream.com/seo
Posted by: hathawaygrainky.blogspot.com






0 Response to "How To Set Up Search Engine Optimization"
Post a Comment